What are the advantages of combining silicone with other materials?
- Share
- publisher
- Siliconeplus Editor
- Issue Time
- Jan 3,2025
Summary
The main advantage of combining silicone with other materials is improved functionality and versatility in products, enabling better durability, flexibility, and industry-specific performance.
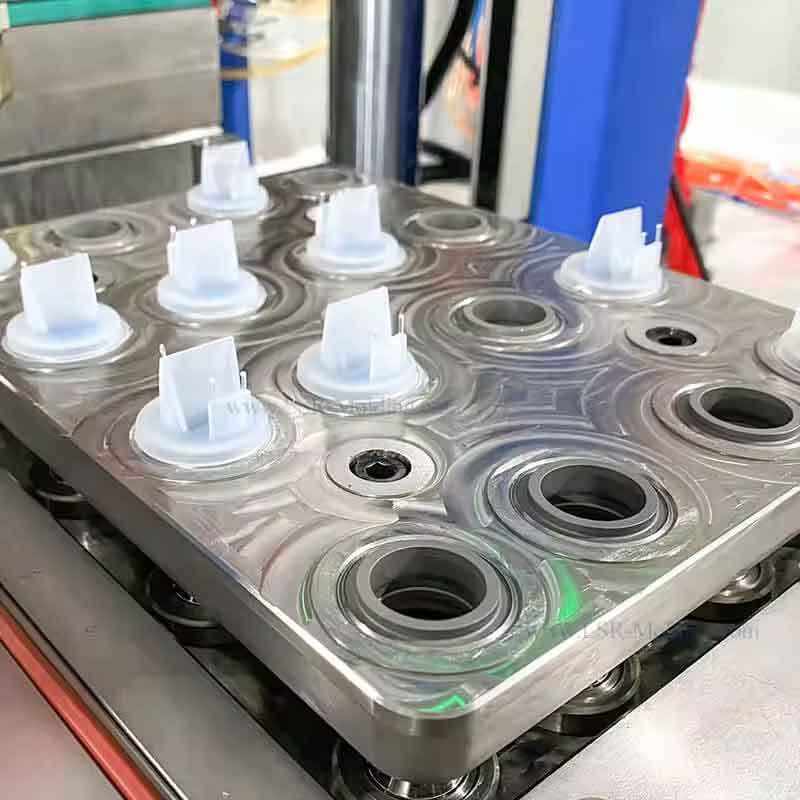


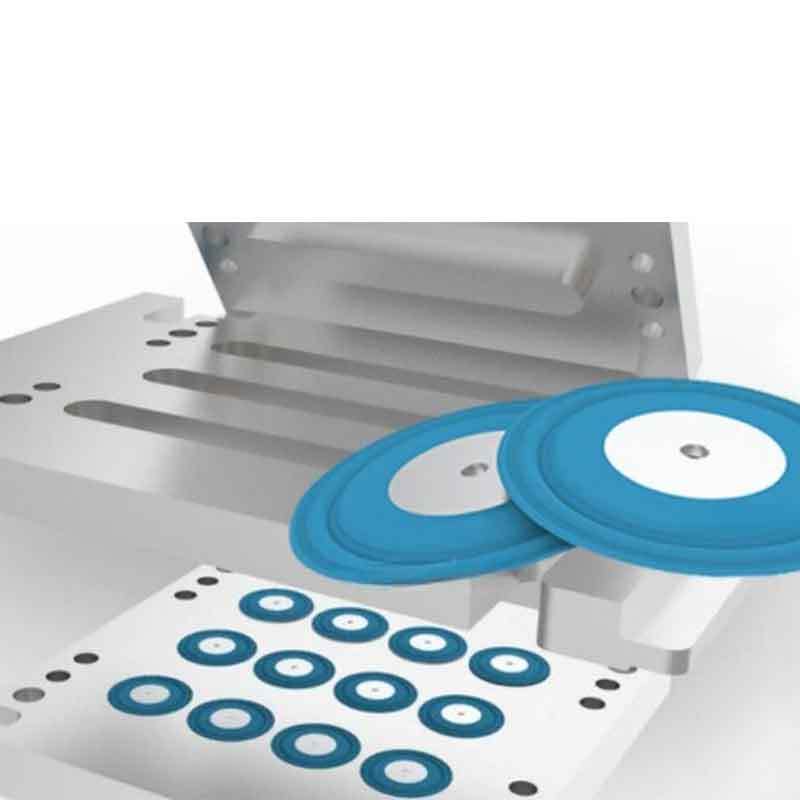
Combining silicone with other materials unlocks new possibilities in product design. It enhances performance and durability, while solving challenges across industries such as electronics, automotive, and healthcare.
The main advantage of combining silicone with other materials is improved functionality and versatility in products, enabling better durability, flexibility, and industry-specific performance.
By blending silicone with plastics, metals, or flexible circuits, we can address specific performance requirements. Let’s explore how these combinations work.
What are the advantages of addition silicones?
Addition silicones are widely used in various applications due to their advanced properties. They offer better thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to other silicones.
The key advantages of addition silicones include excellent thermal stability, low shrinkage, and resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for industrial and medical applications.
Dive Deeper into Addition Silicones
Addition silicones, also known as platinum-cure silicones, are often used in high-precision molding and medical devices. They are ideal for products that need biocompatibility and high accuracy in dimensions.
| Feature | Benefit |
| Low Shrinkage | Maintains dimensional accuracy in products. |
| High Chemical Resistance | Suitable for harsh environments or contact with reactive substances. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs well in high-temperature applications like electronics. |
Addition silicones are also non-toxic and safe for skin contact, which makes them a go-to material for prosthetics and wearable medical devices.
What is silicone not compatible with?
While silicone is versatile, it doesn’t bond well with all materials. Understanding these limitations helps us make better design choices.
Silicone is not compatible with certain non-porous materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, and fluoropolymers due to their low surface energy.
Dive Deeper into Silicone Incompatibilities
Silicone's inability to bond with some materials is primarily due to surface chemistry. For example, plastics like polypropylene and fluoropolymers have non-stick surfaces, which prevent strong adhesion.
Why Does Compatibility Matter?
Adhesion Challenges: Poor bonding leads to weak joints, limiting the structural integrity of products.
Application-Specific Needs: For example, in medical applications, incompatible materials could lead to device failure or safety risks.
Solutions to Overcome Incompatibility:
Use primers or adhesives designed specifically for silicone-to-plastic bonding.
Modify the surface of the material through plasma treatment or roughening techniques.
Does silicone react with other elements?
Silicone's chemical stability is one of its defining characteristics. But under certain conditions, it can react with specific elements.
Silicone is generally inert, but it may react with strong acids, bases, and some organic solvents, leading to degradation.
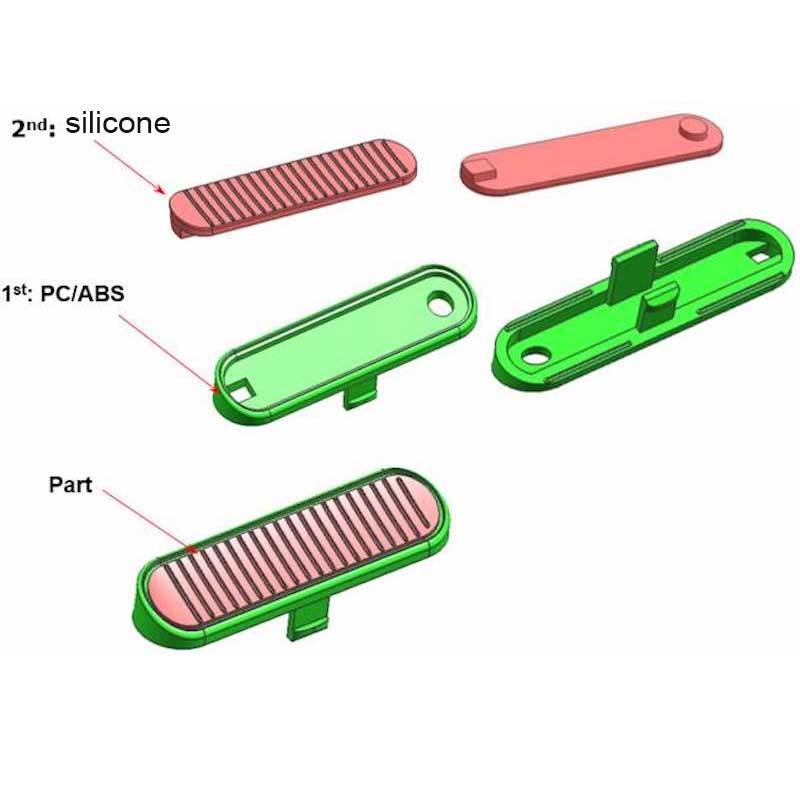
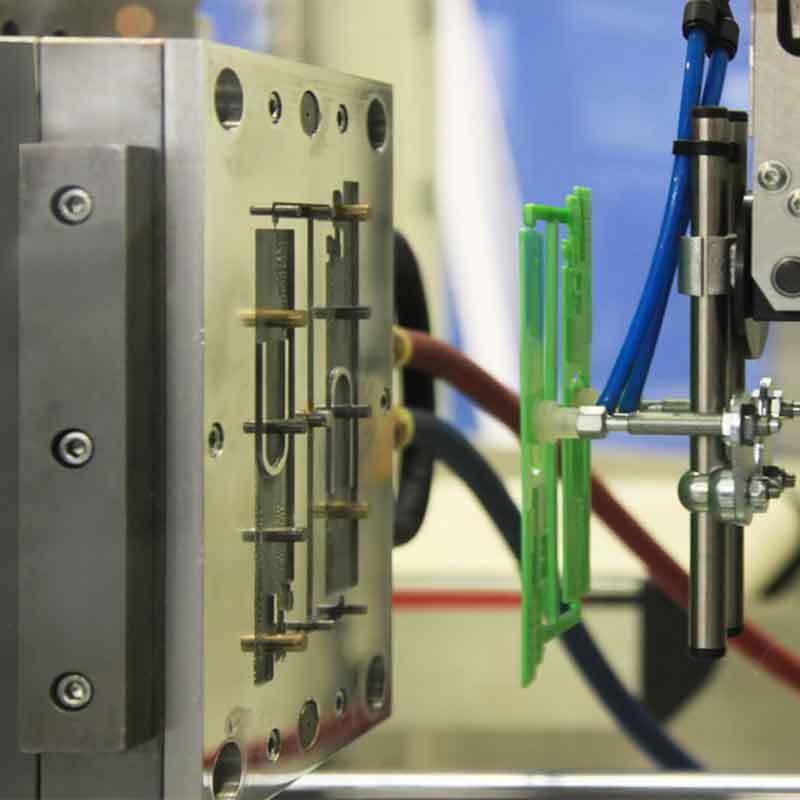
Dive Deeper into Silicone’s Reactivity
Silicone has a unique backbone of silicon and oxygen atoms, making it highly stable. However, extreme conditions can break this stability.
Common Reactions:
Acid/Base Reaction: Strong acids like hydrofluoric acid can break down silicone.
Oxidation: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures and oxygen can cause surface degradation.
Solvent Attack: Silicone can swell or weaken when exposed to certain organic solvents like toluene.
Understanding these reactions is critical in designing silicone products for harsh environments, ensuring long-term performance.
Can you mix two types of silicone?
Mixing different silicones is a complex process that can yield unique material properties. However, compatibility depends on their chemical formulations.
You can mix two types of silicone, but their compatibility and curing mechanisms must align to achieve a consistent material.
Dive Deeper into Silicone Mixing
Mixing two silicones with different curing systems (e.g., addition-cure and condensation-cure) can result in incomplete curing or material instability.
Key Considerations When Mixing Silicones:
Curing System: Ensure both silicones use the same catalyst type (platinum-cure or tin-cure).
Viscosity: Different viscosities can affect mixing consistency and final properties.
Applications: Test the mixed material for performance under intended use conditions.
Practical Tips for Mixing:
Use a precision scale to maintain the correct ratio.
Mix thoroughly to ensure uniformity.
Perform small-batch tests before large-scale production.
By carefully selecting and combining silicones, we can create hybrid materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
Conclusion
Combining silicone with other materials unlocks immense potential across industries. By understanding its compatibility, unique properties, and blending possibilities, we can push the boundaries of innovation in design and performance.