How does silicone injection molding work?
- Share
- publisher
- Siliconeplus Editor
- Issue Time
- Dec 17,2024
Summary
Silicone injection molding forms complex parts by injecting liquid silicone rubber (LSR) into molds under heat and pressure, ensuring precision and consistency in mass production.
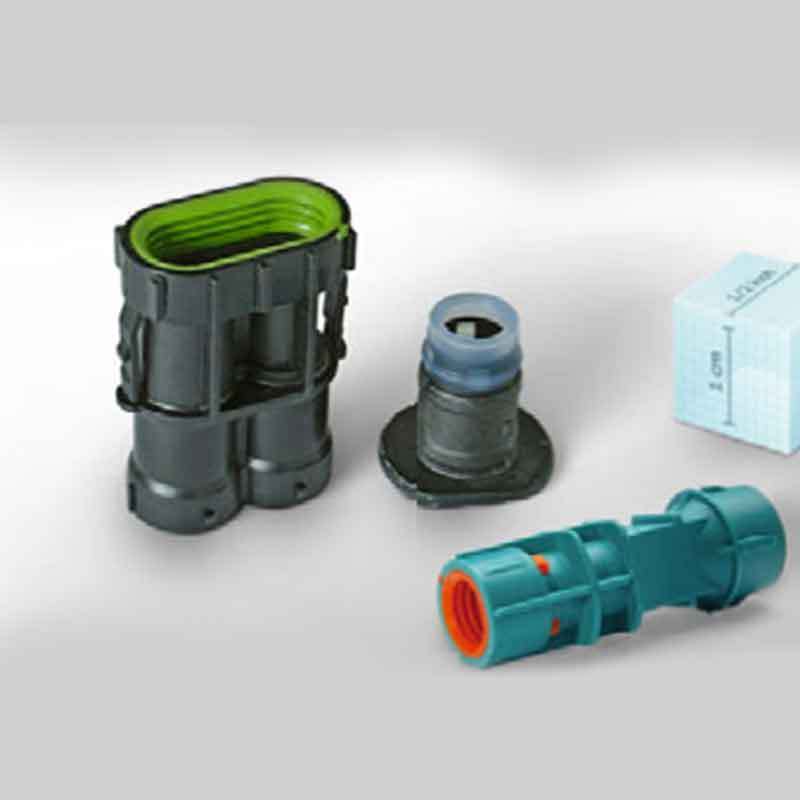

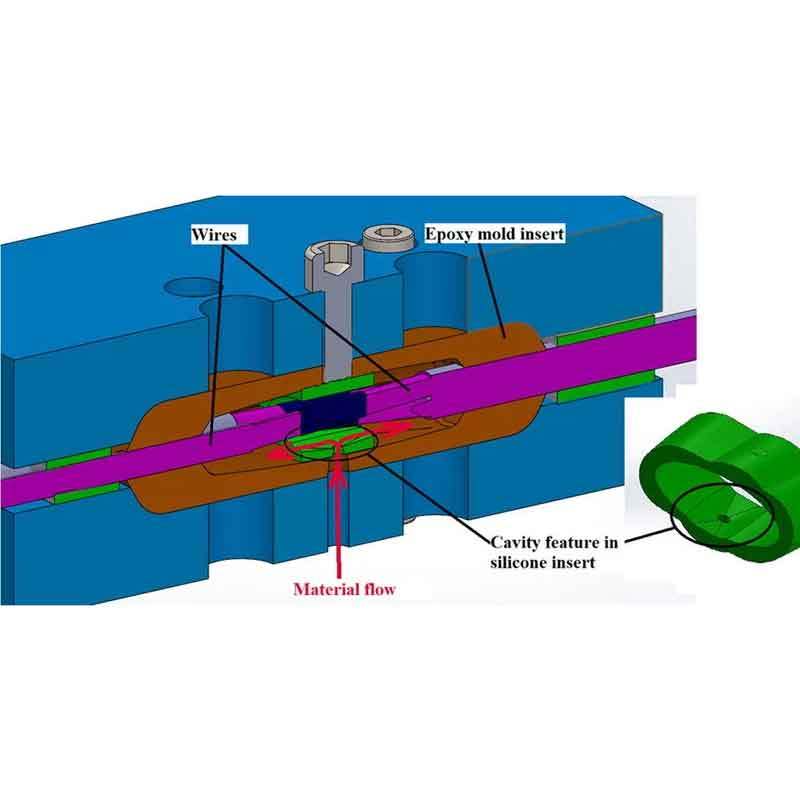
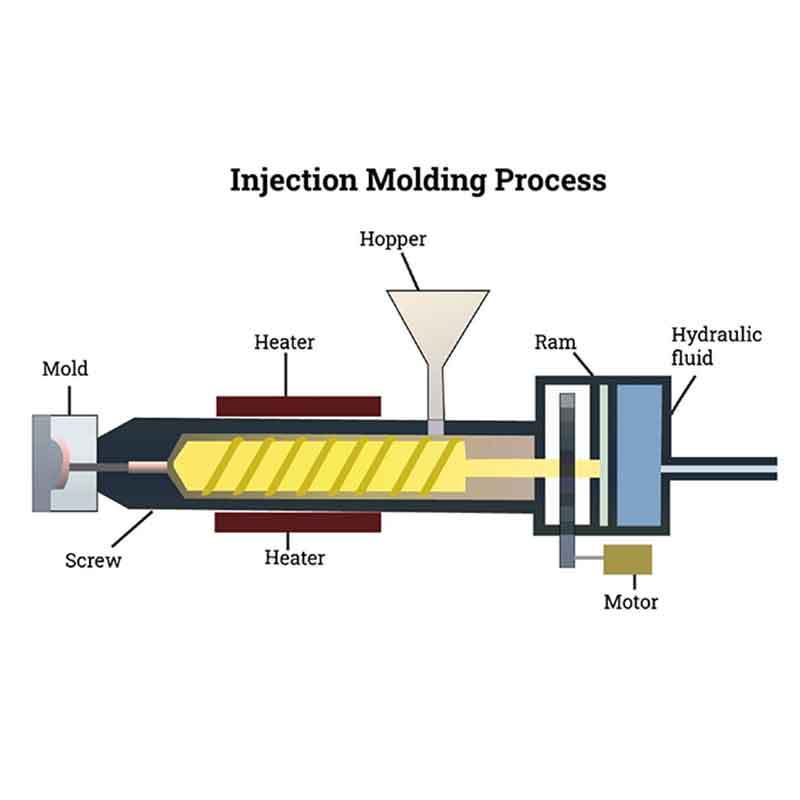
Silicone injection molding is a versatile manufacturing technique used to create complex silicone parts. By applying heat and pressure, silicone is injected into molds to form precise shapes. But how exactly does this process work?
Silicone injection molding involves injecting liquid silicone rubber (LSR) into a mold cavity. The material cures to create a final product. The process ensures high precision and consistency in mass production.
Now that we have a basic idea of how silicone injection molding works, let's take a closer look at its specific steps and processes. Understanding these stages can help improve efficiency and product quality.
What is the process of silicone injection molding?
Before we delve into the intricate details, it’s important to understand the basic steps involved in silicone injection molding. How do raw materials transform into finished parts?
The silicone injection molding process starts with liquefied silicone rubber (LSR) being injected into a mold. This silicone is then cured and cooled to form solid, durable parts.
Silicone injection molding is designed for high-precision manufacturing. The first step involves preparing the silicone material, which is often mixed with a curing agent. This mixture is then injected into a mold cavity using a specialized injection machine. The material fills the mold under high pressure, ensuring an exact fit.
After the injection, the mold is heated to a specific temperature, allowing the silicone to cure and harden. This curing process is crucial, as it determines the material’s final properties, such as its flexibility and durability.
Steps involved:
|
Step
|
Description
|
Material Preparation | LSR is mixed with a curing agent |
Injection | LSR is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. |
|
Curing
|
Heat is applied to cure the silicone.
|
|
Cooling
|
The mold cools to solidify the silicone.
|
Ejection | The finished part is ejected from the mold. |
How does silicone molding work?
How does silicone molding differ from traditional injection molding? Is the process really that much more complex?
Snippet paragraph for h2: Silicone molding is similar to traditional injection molding but uses liquid silicone rubber (LSR) instead of thermoplastics. It requires specific molds, temperatures, and curing techniques to ensure optimal results.
Silicone molding uses the same fundamental principles as traditional injection molding, but it requires some unique adjustments. For example, while thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped, silicone rubber must be cured to solidify. This means that, unlike plastic injection molding, silicone parts undergo a curing process at high temperatures. The process also often demands more precise control of pressure and heat to ensure that the silicone flows smoothly and evenly into the mold.
One important advantage of silicone molding is its ability to create parts that are flexible, durable, and capable of withstanding extreme conditions such as high temperatures or chemical exposure.
How does injection molding work step by step?
Let's break down the entire injection molding process. What are the critical steps that lead from raw material to finished product?
Injection molding typically involves five main steps: material preparation, injection, cooling, curing, and ejection. Each step plays a crucial role in shaping and forming the final silicone product.
The step-by-step process of silicone injection molding begins with preparing the liquid silicone rubber (LSR) material. LSR is a two-part material that includes the base silicone and a curing agent, which together form the final product. Once prepared, the LSR is injected into a heated mold cavity.
The silicone fills the mold under high pressure, and as the mold is heated, the silicone begins to cure, turning from a liquid to a solid rubber state. After curing, the mold cools and the finished part is ejected. The entire process can be completed in seconds to minutes depending on the complexity of the part.
How does silicone curing work?
Curing is a critical part of silicone injection molding, but how does the curing process actually work? What role does heat and time play?
Silicone curing involves a chemical reaction that turns liquid silicone into a solid, flexible material. Heat and time control the rate of this reaction, ensuring the final part has the desired properties.
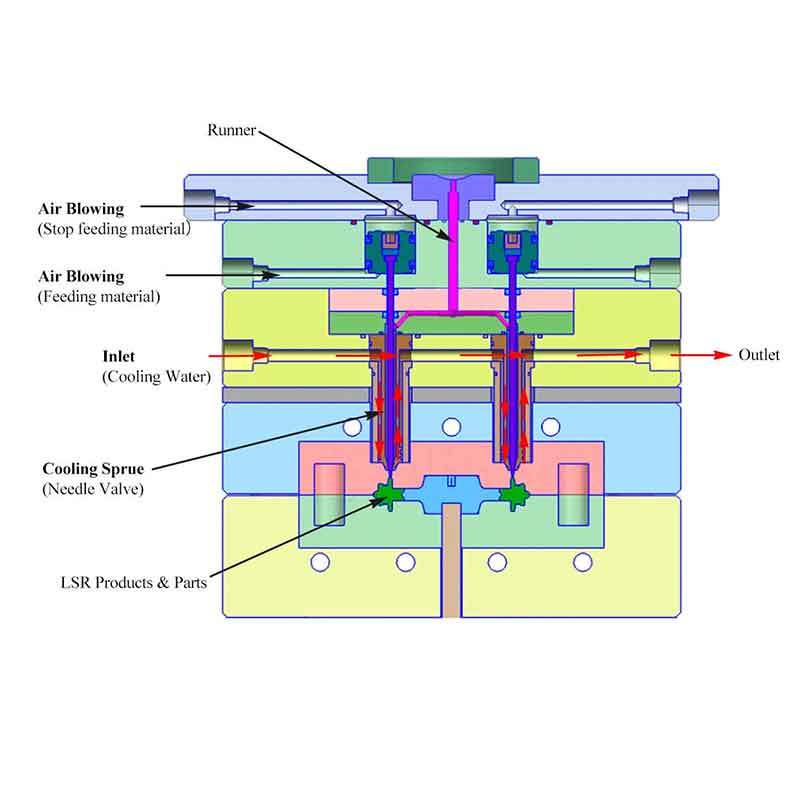
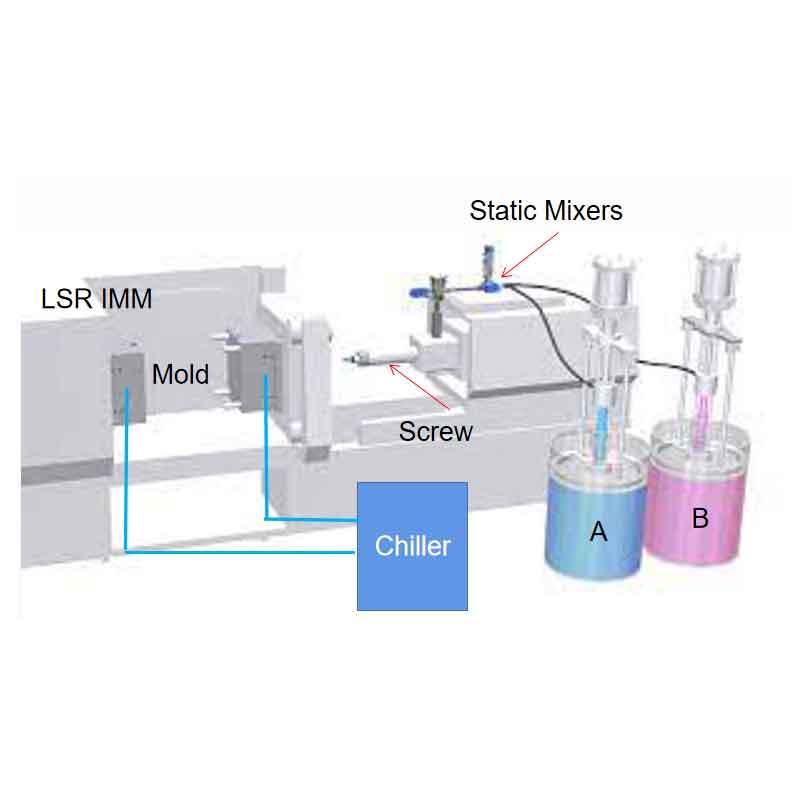
The curing process of silicone in injection molding is a key factor in achieving the desired material properties. Silicone rubber is cured by applying heat, which activates the curing agent mixed with the base silicone. This process causes the molecules in the silicone to cross-link, forming a solid, rubbery structure.
Curing can occur at different temperatures and times, depending on the specific silicone material being used and the properties required for the final product. The mold is typically heated to temperatures ranging from 150°C to 200°C, and the curing process usually takes anywhere from a few minutes to 30 minutes.
The flexibility and durability of the final silicone product depend heavily on this curing stage. Proper control of the heat and curing time ensures that the silicone retains its strength and flexibility, which is essential for industries like automotive, medical, and electronics.
Conclusion:
In summary, silicone injection molding is a precise and efficient method for producing high-quality silicone parts. By understanding each step—from material preparation to curing—you can ensure that the final product meets your specific needs.