How does silicone injection molding work?
- Share
- publisher
- Siliconeplus Editor
- Issue Time
- Dec 7,2024
Summary
Silicone injection molding may sound complex. This manufacturing process transforms raw silicone into precise, durable components for various applications. Let’s dive in and explore how it works.
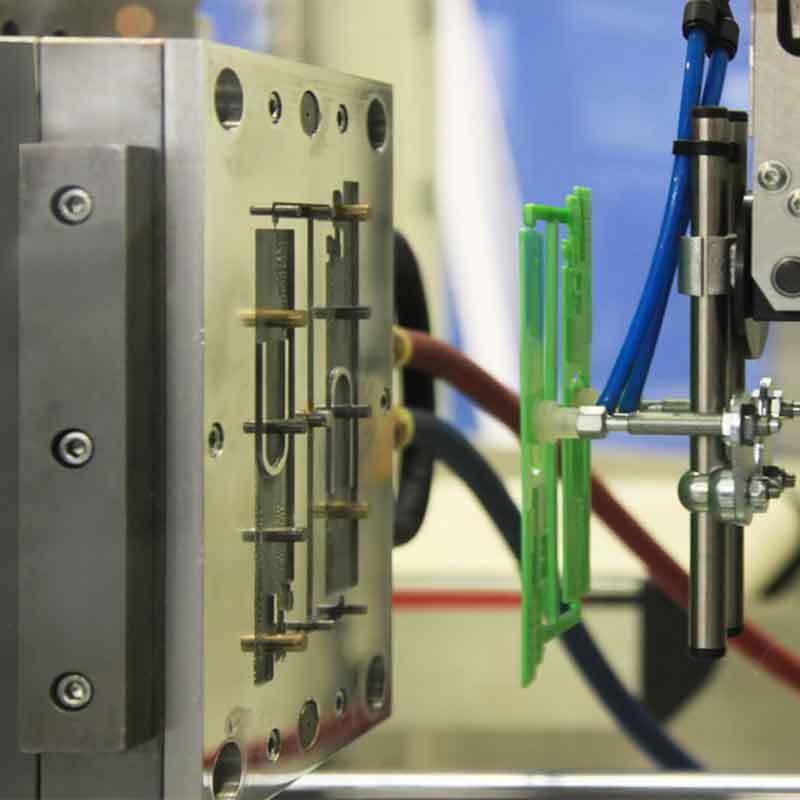
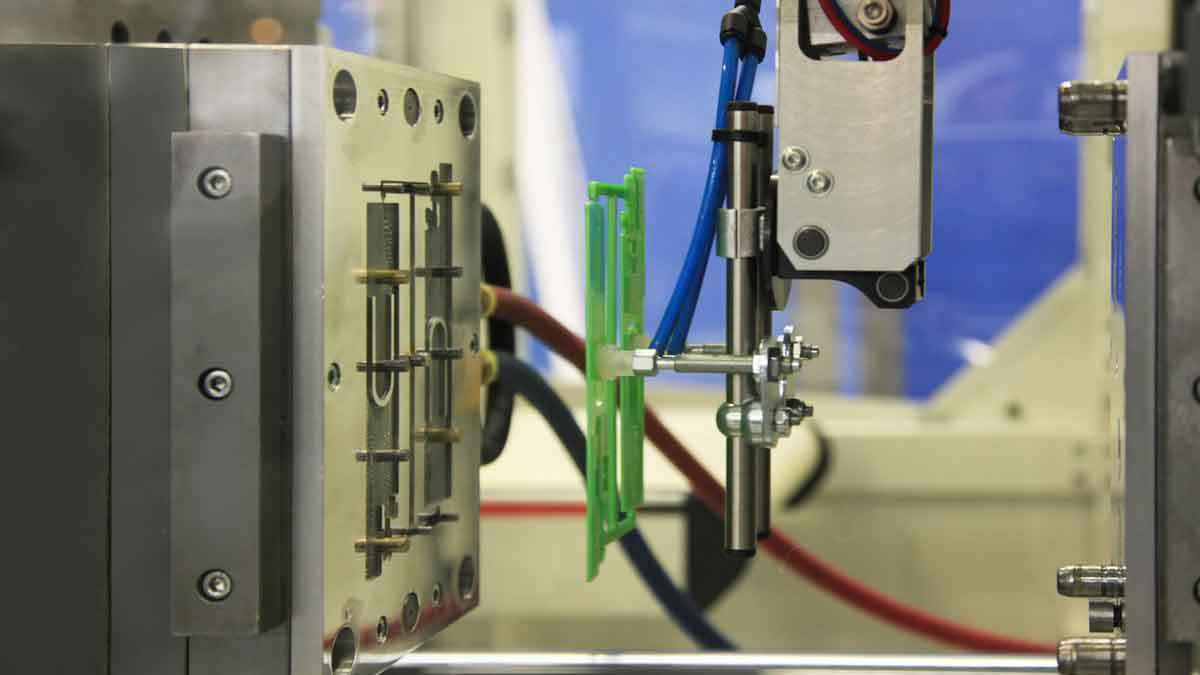
Silicone injection molding may sound complex, but it’s revolutionizing industries. This manufacturing process transforms raw silicone into precise, durable components for various applications. Let’s dive in and explore how it works.
Silicone injection molding works by heating and injecting liquid silicone rubber (LSR) into molds, curing it under pressure to create accurate, durable parts.
From electronics to medical devices, understanding this process helps businesses create innovative products with silicone’s unique properties.
[Table of Contents]
.How is silicone injection molded?
.How does a silicone mold work?
.How does silicone curing work?
.What is the process of silicone compression molding?
How is silicone injection molded?
Silicone injection molding relies on precise machinery and materials to ensure accurate production. It’s a blend of technology and craftsmanship.
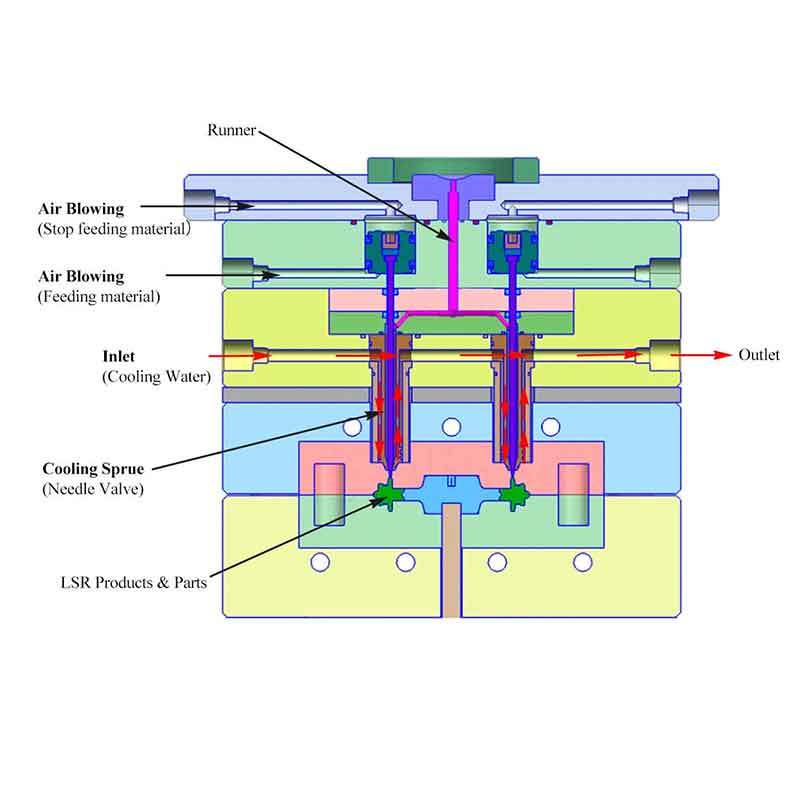
Silicone injection molding involves feeding liquid silicone rubber (LSR) into a heated mold cavity, where it solidifies to form durable, custom-shaped parts.
Dive deeper into the process:
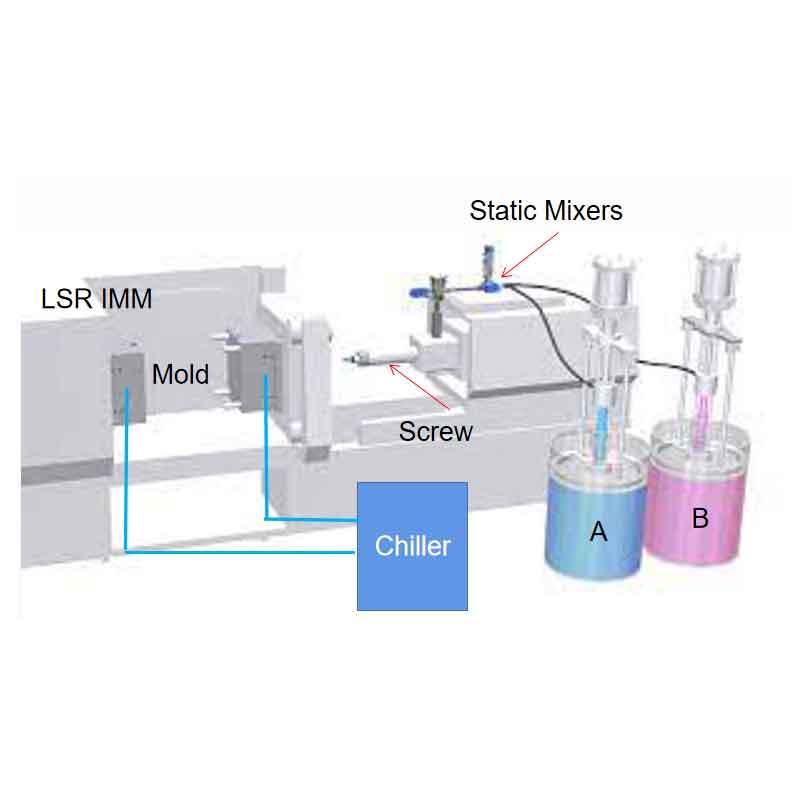
Material preparation: The process starts by preparing LSR, a two-part liquid material that’s mixed together for molding.
Injection and molding: The material is injected into a pre-heated steel mold under controlled pressure. This ensures precise shapes and dimensions.
Curing: Silicone cures at high temperatures, solidifying the material.
Demolding and finishing: Once cured, the parts are removed, inspected, and trimmed for precision.
This process is highly efficient for creating intricate designs, ensuring minimal waste and consistent quality.
How does a silicone mold work?
Silicone molds are the backbone of the injection molding process. They shape the raw material into functional, detailed components.
Silicone molds work by shaping liquid silicone under pressure and heat to create precise parts or products.
Why silicone molds are essential:
Durability: They withstand high pressure and temperature during production.
Accuracy: Silicone molds are machined to the exact specifications of the final product.
Versatility: They enable a variety of shapes, sizes, and complexities.
Dive deeper:
Silicone molds are created using advanced CNC machining or EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) to ensure precision. These molds are treated to endure repeated cycles of injection and curing, making them ideal for high-volume production.
How does silicone curing work?
Curing is the final step that turns liquid silicone into a solid, usable product. But how does it happen?
Silicone curing occurs when heat and pressure trigger a chemical reaction in the silicone, transforming it from liquid to solid.


Dive deeper into curing methods:
There are two main curing processes:
Addition curing: Uses platinum catalysts for faster, more consistent curing.
Peroxide curing: Relies on heat to activate curing agents, often used for larger, thicker components.
The choice of curing method depends on the application. Addition curing is preferred for medical and food-grade silicone due to its low byproduct output. Meanwhile, peroxide curing is ideal for robust industrial parts.
What is the process of silicone compression molding?
Compression molding is another popular method for working with silicone. How does it differ from injection molding?
Silicone compression molding involves placing pre-measured silicone material into a mold cavity and compressing it with heat and pressure to form parts.
The step-by-step process:
Material placement: Uncured silicone is placed in the mold cavity.
Compression: The mold is closed, applying pressure to shape the material.
Heat application: High temperatures cure the silicone, solidifying its shape.
Demolding: Finished parts are removed and inspected.
Advantages of compression molding:
Lower setup costs for smaller production runs.
Suitable for thicker or less complex silicone components.
Reduced material waste compared to injection molding.
While compression molding is less automated than injection molding, it’s a reliable alternative for producing silicone parts with specific requirements.
Conclusion
Silicone injection molding transforms raw materials into precise, durable parts for diverse industries. From material preparation to curing and compression molding, each step adds value to the final product. Understanding these processes unlocks new possibilities for innovation.